- Paper speed = 25 mm/s
- One large square = 0.2s
- One small square = 0.04s
- Amplitude = 10 mm/mV
Rate Calculation
- Assuming standard paper speed there are several methods to calculate the heart rate.
- Count number of large squares between consecutive R waves and divide into 300.
- Count number of small squares between consecutive R waves and divide into 1500.
- An ECG recoding captures10 seconds of activity, so you can multiple the number of complexes along the rhythm strip by 6 to estimate the rate, a useful method for irregular rhythms.
Normal Ranges
- PR Interval: 0.12 - 0.2s (3-5 small squares)
- QRS Duration: < 0.12s (3 small squares)
- QTc usually less than half the R-R interval.
- Consider prolonged QTc either > 440ms or > 460ms for males and >470ms for females.
- Considered shortened QTc if < 330ms
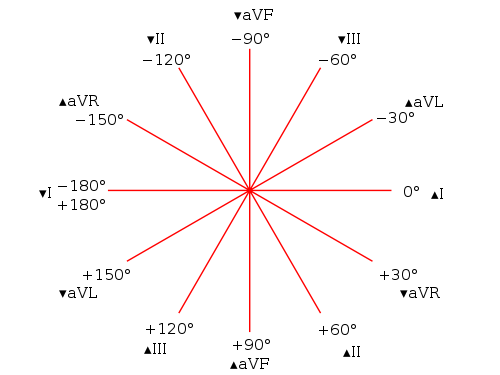
Axis
- Normal: -30 degress to 90 degrees
- Left axis deviation: < -30 degrees
- Right axis deviation: > 90 degrees
- Extreme Axis: 180 degrees to -90 degrees
Hex Axial
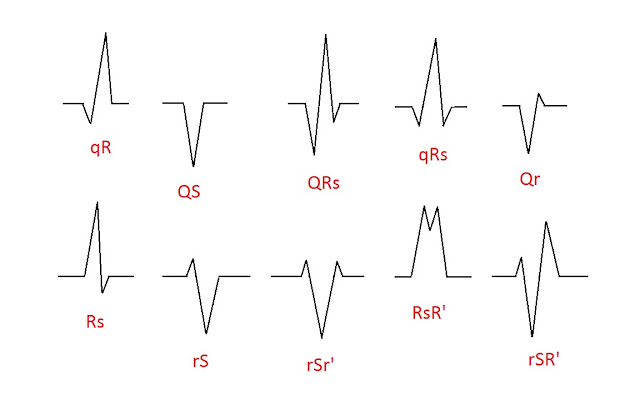
QRS Nomenclature Examples
The QRS complex represents ventricular depolarisation, however, describing the QRS complex with these three letters is often an oversimplification. A QRS complex may not necessarily contain a Q wave, a R wave, or a S wave, and may contain more than one R wave.
The various deflections of the QRS wave can be notarised as follows:
Capitalisation
of the letter indicates tall or deep waves, with small waves notarised with
small letters.
-
Q wave –
any initial negative deflection
-
R wave –
any positive deflection
-
S wave –
any negative deflection after a R wave
-
R’ wave –
any positive deflection that follows an S wave
-
QS complex
– if there is only a single negative deflection
References
- Chan T, Brady W, Harrigan R, Ornato J, Rosen P (2005), ECG in Emergency Medicine and Acute Care, 1st Edition, Elsevier Mosby.
- Hampton J (2003), The ECG in Practice, 4thEdition, Churchill Livingstone.
- Surawicz B, Knilans T (2008), Chou’s Electrocardiography in Clinical Practice, 6th Edition, Saunders Elsevier.
- Morris F, Edhouse J, Brady W, Camm J (2003), ABC of Clinical Electrocardiography, 1st Edition, BMJ Books.